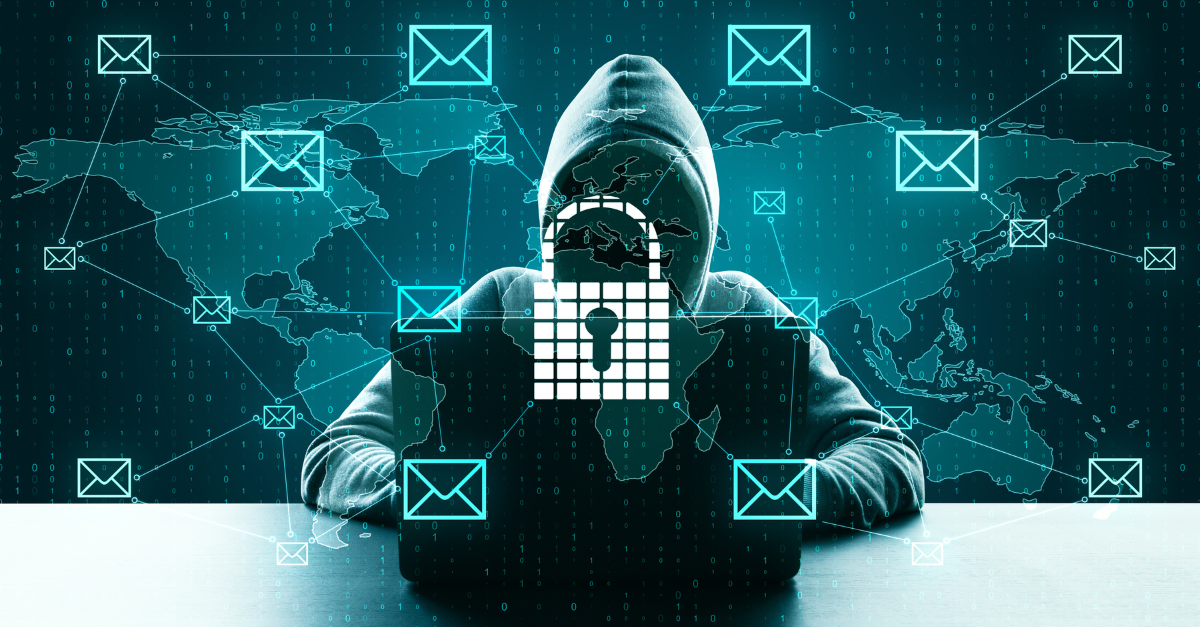
October is Cyber Security Awareness Month, a fantastic opportunity for law firms to review and enhance their cyber security measures, as they are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive information they handle. By staying informed about the latest cyber threats and adjusting security practices, you can effectively safeguard your firm and clients.
Here’s a rundown of prominent cyber security trends and events that have impacted the legal industry in recent years and lessons legal professionals can draw from them.
1. Ransomware Attacks Targeting Law Firms

.
Trend Overview
Ransomware remains one of the most significant cyber security threats to law firms. Cyber criminals deploy malware to encrypt a firm’s data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid. Increasingly, these attackers “double-extort” their victims by threatening to release sensitive client data to the public if firms do not pay an additional ransom.
Case Study: Campbell Conroy & O’Neil, P.C. (2021)
In 2021, Campbell Conroy & O’Neil, a major U.S. law firm, experienced a ransomware attack that exposed the sensitive data of clients, including several Fortune 500 companies. The attackers accessed personally identifiable information (PII), including Social Security numbers, passport numbers, and medical records. The firm had to disclose the incident and notify affected parties, leading to a dent in their reputation.
Lesson for Law Firms
Comprehensive backups and incident response plans are crucial. Additionally, data encryption and regular security audits can minimize the impact of such breaches.
Resources
-
- Ransomware: How to prevent and recover (Government of Canada)
- How can I protect against ransomware? (CISA, USA)
- Protect your PC from ransomware (Microsoft)
2. Insider Threats and Data Mismanagement

.
Trend Overview
Insider threats occur when a current or former employee, contractor, or partner with access to sensitive information inadvertently or intentionally misuses it. Because they stem from trusted individuals, insider incidents are often harder to detect than external attacks.
Case Study: Mossack Fonseca (2016)
The Panama Papers leak, one of the most significant data leaks in history, was orchestrated by an anonymous whistleblower who used the pseudonym “John Doe.” The identity of John Doe was never revealed, but there is speculation that they might have been an insider. This incident occurred in 2016 and remains a stark reminder of the devastation an insider breach can cause. It exposed sensitive financial dealings of individuals and entities worldwide, causing significant reputational and legal damage. Once the world’s fourth-largest provider of offshore financial services, Mossack Fonseca had to close its doors in March 2018.
Lesson for Law Firms
Implement strict access controls, regularly audit employee access to sensitive information, and conduct thorough background checks on employees, contractors and partners. Consistently educating your team about cyber security best practices is also essential for reducing accidental data leakage.
Resources
-
- Modern approaches to network access security (US, New Zealand and Canadian Governments)
3. Third-Party Vendor Risks

.
Trend Overview
Third-party vendors, such as e-discovery platforms, legal software providers, and document management systems, increase the risk of external vulnerabilities.
Case Study: Epiq Global (2020)
In February 2020, Epiq Global, a prominent legal services provider, suffered a ransomware attack that forced the company to take its systems offline. Epiq’s systems handle sensitive data for numerous law firms, and while they eventually restored systems and reported that client data wasn’t compromised, the incident highlighted the importance of vendor management.
Lesson for Law Firms
Law firms must thoroughly vet third-party providers for their security practices, negotiate strong cyber security clauses in contracts, and monitor vendor compliance regularly. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and data encryption with vendors should also be mandatory.
Resources
One way to effectively mitigate this risk is by deploying a comprehensive practice management solution that enables you to handle sensitive information efficiently while reducing the security risks of using multiple software tools. Unity® Practice Management is a modern, all-in-one cloud-based solution that helps you manage your practice and best serve your clients from intake to invoice. The platform offers best-in-class data encryption and privacy controls, ensuring the security of confidential information.
4. Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks

.
Trend Overview
Phishing and social engineering attacks continue to be among the most common cyberattacks on law firms. Cybercriminals exploit human vulnerabilities by posing as trusted contacts, sending deceptive emails, or using other techniques to extract login credentials or gain access to systems.
Case Study: DLA Piper (2017)
One of the world’s largest law firms, DLA Piper, was crippled by the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017. The attack originated in the DLA Piper Ukraine office, where an individual presumably clicked on something malicious because of an update to accounting software needed for tax filings. The person who did this had administrative privileges, which helped the attack spread. This situation shows how a security breach in one place can have far-reaching effects on global business operations. The firm’s systems were down for several days, severely disrupting its operations.
Lesson for Law Firms
Regular phishing awareness training for staff, deploying email filtering software, and using MFA can help protect firms from phishing attacks. Firms should also ensure that all software, especially from third parties, is kept up to date to avoid exploitation.
Resources
-
- Social engineering (Government of Canada)
- Five ways to step up your law firm’s cyber fitness (Dye & Durham)
- Security culture (KnowBe4)
.
5. Data Privacy Regulations and Compliance Challenges

.
Trend Overview
As data privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to expand, law firms must ensure compliance with these regulations. Failing to meet privacy obligations can lead to significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
Case Study: GDPR Fines for Mishandling Data
Several law firms across Europe have faced hefty fines for GDPR violations. In February 2022, UK-based law firm Tuckers was fined £98,000 for not adequately securing client data, leaving it vulnerable to unauthorized access. The firm fell victim to a ransomware attack, which made parts of its IT system inaccessible and allowed the attackers to encrypt civil and criminal legal case bundles stored on an archive server, as well as the backups. Although the attack only affected an archive server and not the live server, a significant amount of personal data records were compromised, with nearly one million individual files being encrypted.
While the data breach resulted from an external hack and not any intentional action by the firm, the ICO (Information Commissioner’s Office) noted that the security measures in place were inadequate. Specifically, Tuckers did not utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access to servers and files and failed to update software with relevant patches issued by software providers. The ICO also observed a failure to encrypt personal data. Despite Tuckers promptly reporting the breach and taking steps to minimize the impact on data subjects, the ICO deemed the breach serious enough to warrant a fine representing 3.25% of Tuckers’ annual turnover up to June 30, 2022. This incident highlights that failure to comply with data privacy regulations could result in both financial and reputational damage.
Lesson for Law Firms
Law firms must conduct regular data privacy audits, implement clear data retention policies, and ensure they are up to date on all relevant data privacy laws, not just in their home jurisdiction but globally.
Resources
-
- Summary of privacy laws in Canada (Canada)
- GDPR (EU)
- Data protection laws of the world (DLA Piper, for all Countries)
.
Conclusion
Cyber threats facing the legal industry are growing in both volume and sophistication. By constantly investing time and resources in cyber security awareness training, third-party risk management, data privacy compliance, and advanced security technologies, law firms will be equipped to mitigate and respond to these threats
Go to Media